Prostatitis is inflammation of the tissue of the prostate gland, its edema.This is the term determining inflammation of the prostate gland.
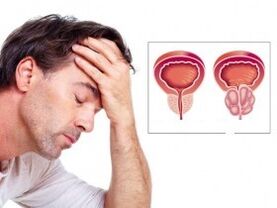
Prostate- Part of the male reproductive system that produces a specific secret that feeds and protect spermatozoa.With the reduction of smooth muscle fibers of the capsule of the prostate and seed bubbles, the seed fluid is released into the urethra - ejaculation (ejaculation).
Prostatitis can develop only in men. Over the past 20 years, the incidence of prostatitis has increased about half, and now, at the dawn of the 21st century, it is suffered by almost half the male population of the Earth aged 20 to 50. It is believed that after 30 years 30% of men suffer from prostatitis, after 40-40%, after 50 - 50%, etc.
Classification of prostatitis:
- spicy;
- asymptomatic inflammation;
- chronic bacterial;
- Inflammatory chronic pelvic pain.
Complaints with prostatitis:
- Various urinating disorders associated with narrowing the lumen of the urethra:
- the difficult start of urination;
- intermittent urination;
- weak stream of urine;
- Urination dropped;
- a sense of incomplete emptying of the urinary puzir;
- involuntary urine leakage.
- Symptoms caused by irritation of the nerve endings:
- rapid urination;
- frequent urination at night;
- urgent urination;
- urination by small ports;
- Urine's irreverion of urination.
- Pain in the lower abdomen, inguinal areas, the inner surface of the hips or lower back, a variety of sexual disorders can occur.
There are several causes of prostatitis:
- sexually transmitted infections: chlamydia, ureaplasma, mycoplasma, herpes virus, cytomegalovirus, trichomonads, gonococcus, genus of the genus Candida, E. coli can affect the urethra and be detected in prostate fabric;
- violation of blood circulation in the pelvic organs (stagnation in the prostate leads to its inflammation);
- Sitting lifestyle (drivers, office employees, officials);
- long sexual abstinence interrupted by sexual intercourse or artificial lengthening of sexual intercourse;
- impaired immunity;
- Frequent hypothermia (lovers of extreme relaxation: diving, surfing, biodar and skiing sport);
- Stress: mental and physical overload;
- violation of allergic status;
- hormonal imbalance;
- deficiency of vitamins and trace elements.
Treatment of acute and chronic prostatitis
While with therapy of acute prostatitis of difficulties, as a rule, there is no, chronic prostatitis of correction is not always lended.
There is a general treatment tactics for conducting patients with acute prostatitis:
- Compliance with bed rest.
- The appointment of antibacterial drugs.
- A ban on prostate massage even in order to obtain a prostate secret.The ban is due to a high risk of sepsis.
- The appointment of drugs aimed at normalizing blood microcirculation, at increasing its fluidity and viscosity.I thank the effect of these drugs, it is possible to achieve an outflow of lymph and venous blood from the inflamed gland, reduce toxic manifestations and remove decay products from the body.
- The oral reception of NSAIDs or other tablet analgesics.They are prescribed to reduce pain.
- In their practice, urologists widely use rectal candles to have an analgesic effect to reduce inflammation.They include the same components as in tablet drugs, but thanks to local administration, the effect is enhanced.You can use candles from prostatitis with propolis.
- If the patient suffers from severe intoxication of the body, the administration of rheological solutions, as well as detoxification agents and electrolytes in a hospital conditions, is indicated.
- Surgical intervention is necessary if the possibility of independent emptying of the bladder is completely absent, or an abscess of prostate has been formed.
The use of antibiotics for the treatment of bacterial prostatitis is mandatory.If the disease begins acutely, there are symptoms of intoxication, then antibacterial drugs are prescribed as quickly as possible, wait for the results of tests for the bacterial flora in this case is inappropriate and dangerous.
The doctor chooses medicines from the group of fluoroquinolons.This can be levofloxacin, ciprofloxacin. The like -like empirical therapy is due to the fact that fluoroquinolones have activity in relation to bacteria that most often provoke prostatitis - this is gram -negative pathogenic flora and enterococci.In addition, fluoroquinolons have a destructive effect on gram -positive and anaerobic bacteria, as well as on atypical infectious agents, for example, on chlamydia.Introducing into the metabolic processes of protein metabolism, the antibiotic destroys their core, leading to the death of microorganism.
Also, these drugs are very effective in terms of treatment of prostatitis, as they have the opportunity to quickly penetrate the tissues of the prostate gland and into the seed bubbles, accumulating there in high concentrations.The therapeutic effect also enhances the fact that the prostate in an inflamed state has very high permeability.
This group of drugs is also replaced if after 24-48 hours from the beginning of their intake the patient's condition did not improve, or if he does not tolerate them well.The drugs of choice in this case are macrolides, antibiotics from a group of cephalosporins or lincosamides.
Increasingly, prostatitis bacteria become insensitive to most modern antibiotics.Because of this, prostatitis is often unable to cure to the end, the disease goes into a chronic form.
If recovery after 14 days from the start of taking medications does not occur, then the treatment regimen should be adjusted again, but the treatment of prostatitis cannot last less than 14-30 days.But the appointment of antibiotics is carried out by the doctor, focusing on the data of the clinical picture of the disease and the results of the bacteriological sowing of the contents of the prostate with the determination of the sensitivity of sowed microorganisms to certain antibiotics.
Complications of prostatitis
The not -alerted prostatitis has every chance to go into a chronic form of prostatitis, and in men over 40, a prostate adenoma can develop, associated with hormonal imbalance (after 40 years in men, the production of testosterone is reduced, and the secretion of estrogen increases).
Prostate adenoma- benign prostate hyperplasia - this is the presence of pathological benign growth of the prostate gland, located in the circumference of the urethra.
Prostate adenoma is one of the most common diseases in elderly men.
During a detailed examination, signs of prostate adenoma aged 40-50 are observed in 25%of men, at 50-60 years old-in 50%, at 60-70 in 65%, at 70-80 years old in 80%, over 80 years old-more than 90%of men.
Manifestations of prostate adenoma
The growth of prostate tissue with age leads to an increase in the organ, which causes narrowing of the urethra and manifests itself as the following symptoms:
- Incorrect and difficulty urinating - urination becomes especially frequent at night.
- The weakening of the urine stream is one of the first symptoms of the disease, which most often remains unnoticed until other symptoms of the disease.
- The feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder is often masked under rapid urination in the morning.Such men complain that, despite the normal frequency of urination during the day, in the morning they have to urinate 3-4 times with an interval of 10-15 minutes.
- Imperial (sudden, hard -to -keeping) urination is one of the symptoms forcing a man to see a doctor.
- Undead and incontinence of urine.
The main differences between prostatitis and prostate adenoma:
| Prostate adenoma | Prostatitis | |
| What happens in the prostate gland? | One or more small knots are formed, which gradually grow and squeeze the urethra. | In the tissue of the prostate gland, inflammation develops. |
| At what age does it occur more often? | Usually after 40 years.Less commonly at a younger age. | Most often in 20-40 years. |
| Why does it arise? | The exact reasons are not fully established.It is considered one of the manifestations of male menopause. | The main reasons:
|
| Features of treatment | They use medications, in severe cases - surgical treatment (excision of overgrown tissue of the prostate gland). | Typically, antimicrobial, anti -inflammatory, painkillers are prescribed. |
Prevention measures
There are also several recommendations that will strengthen male health:
- Physical activity.At least 10 minutes of morning time should be devoted to perform simple charging.The same rule is relevant with sitting work.
- A contrast shower is also an excellent means to improve its well -being.
- As for food, it is necessary to include raw pumpkin seeds in your diet (a phytopreparation based on pumpkin seeds, nettle extract, palm extract + zinc and selenium in capsules. Normalizes the exchange of testosterone and hormonal background, reducing the growth of the iron stroke of prostate. 1 capsule is used in the morning and evening for 1 month, if necessary, re -technique is possible.It normalizes urination, relieves pain, restores potency.
- It is necessary to refuse pickled products, especially this is true for various sauces with the addition of vinegar - mayonnaise, ketchup, salting, marinades, etc.
- The fight against excess weight (improves metabolism throughout the body).
- Exclude the wearing of things tight in the crotch of things: panties, pants.
Exclude random sexual intercourse as a means of preventing sexual infections.Sexual life should be established.Incomplete sexual acts, unrealized erections are very harmful.